Prevalence of hyperuricemia and its risk factors in healthy male adults from Abakaliki metropolis, Nigeria
Abstract
Chinwe Ewenighi, Uchechukwu Dimkpa, Uchechukwu Ezeugwu, Joel Onyeanusi, Linus Onoh, batunde adejumo, Gladys Onoh
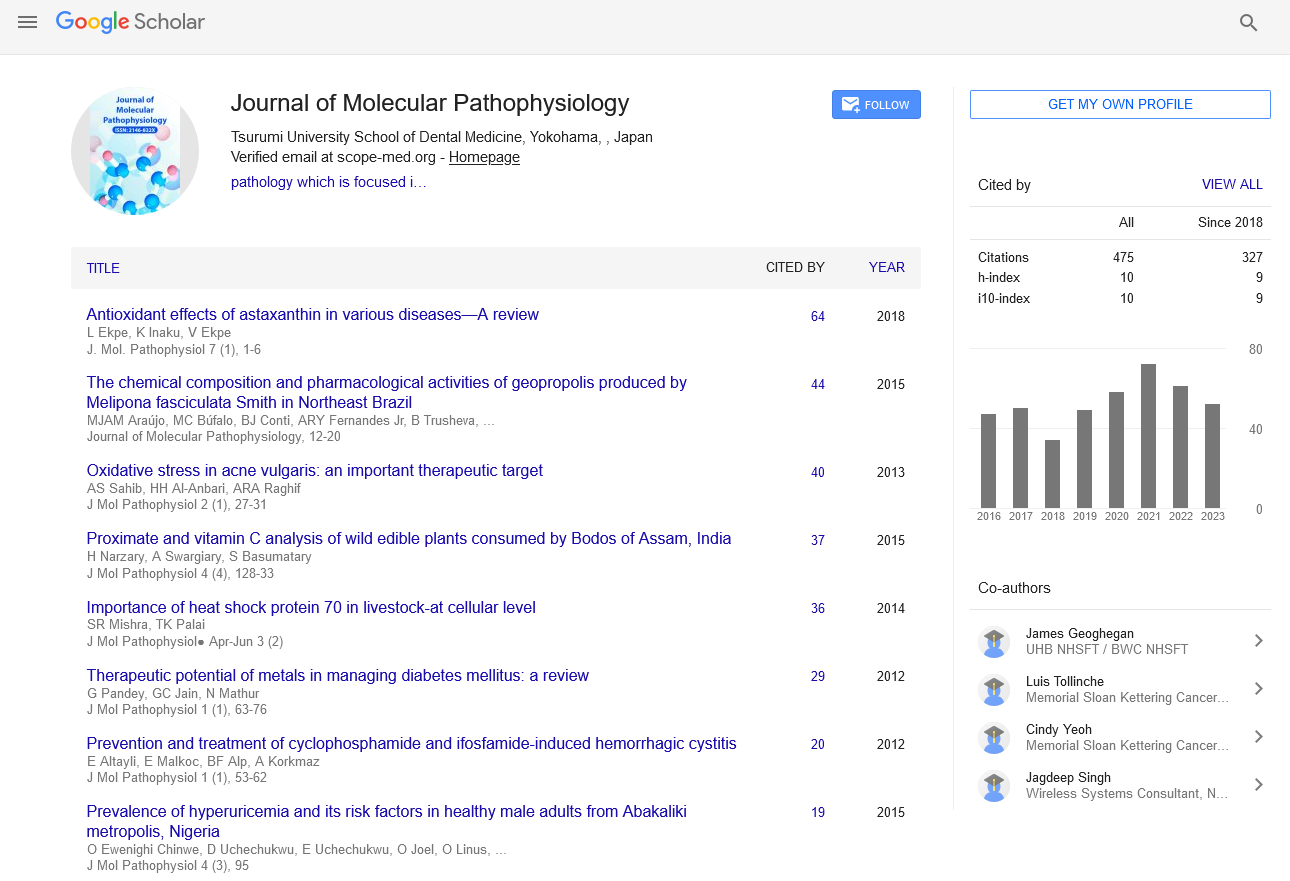
Aim: To estimate the prevalence of hyperuricemia and some risk factors among men in Abakaliki metropolis, Ebonyi State Nigeria. Method: A total of 288 males within the ages of 18-75 years participated in the study. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated from weight and height measurements. Serum uric acid level was measured by enzymatic colorimetric method. Result: The prevalence of hyperuricemia in the study population was 35.8% with serum uric acid level of 7.62 ± 1.49 mg/dl. There was significant positive relationship between uric acid concentration and age (R = 0.307; p < 0.01) and BMI (R = 0.204; p < 0.05). In the hyperuricemic group, mean uric acid concentration was significantly greater in the obese and overweight groups compared to the normal weight group. Data also indicated significantly greater uric acid level in the elderly (p < 0.001) and middle-aged (p < 0.001) compared to the young adults in ‘all subjects’ data but not in the hyperuricemic group. The odds of hyperuricemia was higher in overweight/obese subjects compared to the normal weight group (p < 0.05) and in older subjects of age ≥ 36 yrs compared to younger adults of ages 18-35 yrs (p < 0.001). Conclusion: This study indicated a relatively high prevalence of hyperuricemia in adult males in Abakaliki metropolis Eastern Nigeria. Our data also suggested that overweight/obese and older adult males are at greater risk of hyperuricemia compared to normal weight and younger adults respectively.
https://bluecruiseturkey.co
https://bestbluecruises.com
https://marmarisboatcharter.com
https://bodrumboatcharter.com
https://fethiyeboatcharter.com
https://gocekboatcharter.com
https://ssplusyachting.com