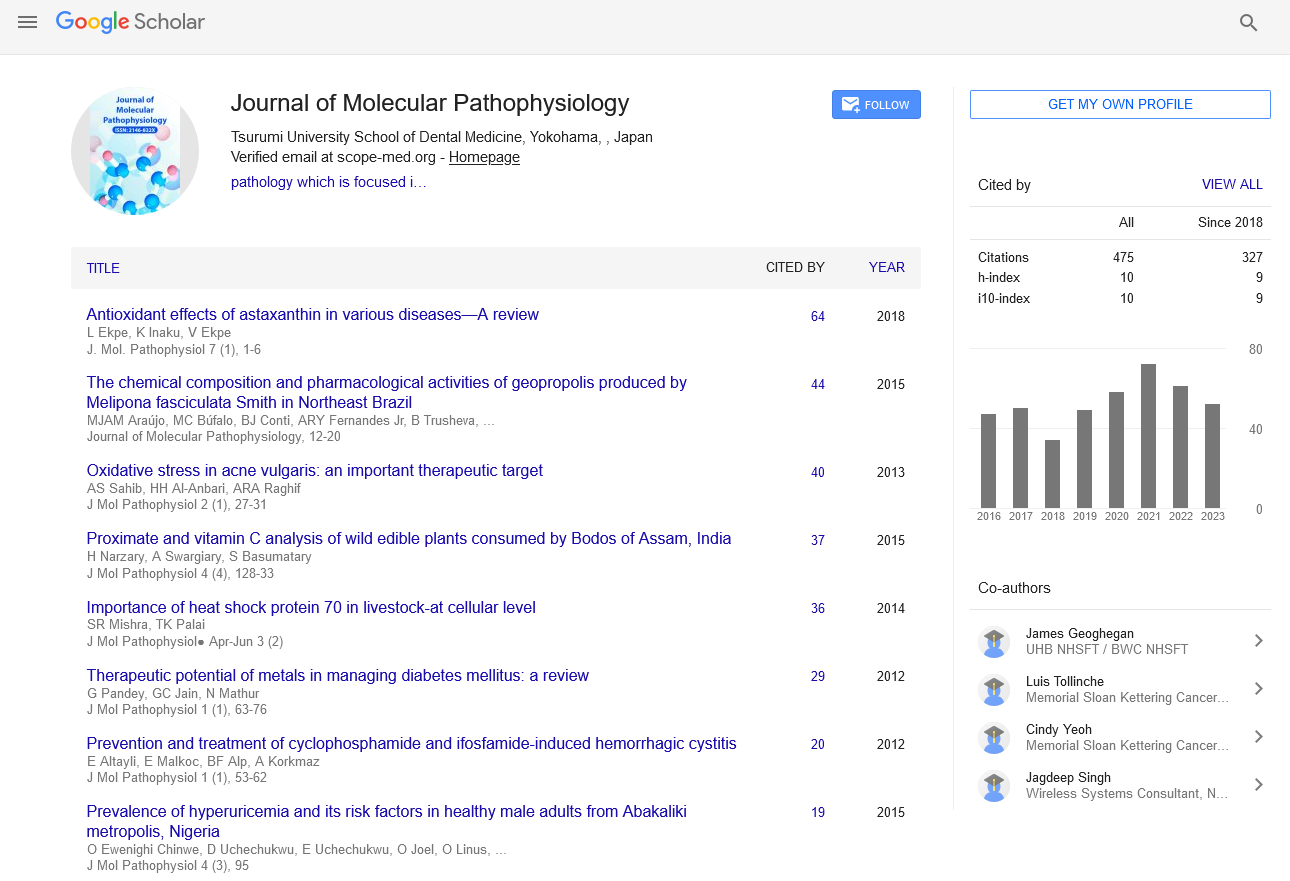
Perspective - Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology (2022)
A Note on Dermatopathology
Stephen Joseph*Stephen Joseph, Department of Neurosurgery, Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, USA, Email: stephenjfowler@ac.uk
Received: 03-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. JMOLPAT-22-41714; Editor assigned: 07-Feb-2022, Pre QC No. JMOLPAT-22-41714 (PQ); Reviewed: 23-Feb-2022, QC No. JMOLPAT-22-41714; Revised: 01-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. JMOLPAT-22-41714 (R); Published: 08-Mar-2022
About the Study
Dermatopathology is a branch of dermatology and pathology that focuses on the microscopic and molecular examination of cutaneous diseases. It also includes easy-to-understand evaluations of the functional causes of skin and pores and skin diseases. Dermatologists can identify most skin conditions based on their appearances, anatomic distributions, and behavior. When such prerequisites don’t allow for a conclusive evaluation, a skin sample is taken to be viewed under a microscope or subjected to one-of-a-kind molecular analyses. This well-known technique depicts the illness’s histology and leads to a specific diagnostic interpretation. More specialists testing on biopsies may be required at times, including immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy, flow cytometry, and molecular- pathologic evaluation. Dermatopathology is used in a variety of situations. Some biopsies are interpreted by the dermatologists who obtained them; some are transferred to pathology laboratories and interpreted by today’s pathologists or dermatopathologists, while still others are interpreted in specialized dermatopathology laboratories.
Dermatopathologists must have a broad base of knowledge in scientific dermatology and be knowledgeable with a variety of specialized fields of medicine. Multiple papulonodular skin lesions at the outset can indicate the presence of serious benign and malignant problems. Although the clinical feature of the lesions may also guide the doctor in the progress of one disease or another, the diagnosis is best verified through histopathologic examination of a biopsy. The examination of diseases is known as pathology. It entails an examination of the causes, course, and progression, as well as any complications that arise as a result of the illness. The epidermis, dermissubcutis, fascia and underlying tissues of the specimen are all investigated in detail. The pathologist may also present you with a definite evaluation or a list of serious possible reasons, generating a differential evaluation, based on the data. The final evaluation, or list of several plausible reasons, is developed through the integration of scientific data on the facet of pathological results, resulting in a differential evaluation. The signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis might vary depending on a person’s age and the severity of the situation, and they can also vary depending on how an individual lives. The majority of the time, eczema symptoms, indications, and symptoms are minor. This should make breakouts much more difficult to detect.
Eczema is a skin condition that causes your pores and skin to become dry, pink, itchy, and rough. It is considered to be one of many types of dermatitis. Eczema wreaks havoc on the skin’s pores and skin barrier. This loss of barrier function makes your pores and skin more sensitive, making them more susceptible to infection and dryness. When people ask about eczema, they usually mean atopic eczema, which is characterized by dry, itchy skin and is frequently accompanied by a pink rash. This is the most common and chronic eczema location and shape.
When the irritant is eliminated, the infection goes away with it. Fingers and soles of the feet are all affected by dyshidrotic dermatitis. It causes itchiness, scaliness, and flaking of the skin, as well as pink, cracked, and painful spots. Women are increasingly encountering this issue. Eczema symptoms and signs and symptoms include itchy, pink, and dry pores and skin as a result of infection. Despite the fact that adults can have it, it is most commonly decided in children. It’s also known as atopic dermatitis, and it’s treated with a combination of oral drugs, steroid creams, and light treatment.
Copyright: © 2022 The Authors. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.